Liquid nitrogen, with its impressive properties and varied applications, has captivated the attention of industries worldwide. While there are several methods to produce liquid nitrogen, combining the Air Unit Separation (AUS) process with liquid nitrogen generators offers a holistic approach to efficient manufacturing. In this article, we will delve deep into this merged process to provide an in-depth understanding of the liquid nitrogen manufacturing process.

An Overview of Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is essentially nitrogen in its liquid state. It exists at an extremely low temperature of approximately -196°C (-321°F). Known for its rapid cooling properties, it has become indispensable in various applications such as cryopreservation, cooling, and even culinary arts.
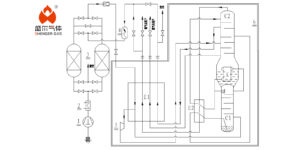
Air Unit Separation (AUS)
AUS is the primary method employed in the production of large volumes of liquid nitrogen. The process can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Air Filtration: The initial step involves filtering the atmospheric air to remove any dust or impurities.
- Air Compression: Post-filtration, the air is compressed, increasing its pressure and reducing its volume.
- Cooling: The compressed air is then cooled to approach its liquefaction point.
- Distillation: The cooled, compressed air is passed into a distillation column where nitrogen is separated from other atmospheric gases due to its unique boiling point.
Liquid Nitrogen Generators
Liquid nitrogen generators utilize a different methodology. Instead of distillation, they rely on the principle of membrane separation or pressure swing adsorption (PSA):
- Membrane Separation: This involves passing air through specialized membranes. Nitrogen molecules, being smaller, pass through these membranes more easily than oxygen molecules, leading to a concentration of nitrogen on one side.
- Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA): In PSA, compressed air is passed through a column filled with a material that preferentially adsorbs oxygen over nitrogen. By quickly altering the pressure, oxygen can be desorbed, leaving behind nearly pure nitrogen.
Combining AUS with Liquid Nitrogen Generators
The idea of merging AUS and liquid nitrogen generators arises from the necessity to enhance efficiency and production volumes. By doing so, the combined process can leverage the strengths of both methods:
- Efficiency: While AUS is adept at handling large volumes, liquid nitrogen generators, particularly those based on PSA, can produce high purity nitrogen. The combined process ensures large volume production without compromising purity.
- Scalability: For industries with varying demands, this combined process allows scalability. During peak demands, both processes can be run simultaneously, ensuring a constant supply.
- Redundancy: If one system faces operational issues, the other can still produce liquid nitrogen, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Applications
Liquid nitrogen manufactured through this integrated process can cater to a plethora of industries, from healthcare, where it’s used in cryogenic storage, to food industries, where it’s utilized in rapid freezing and culinary delights.
Conclusion
The liquid nitrogen manufacturing landscape is ever-evolving. Combining the robustness of the AUS process with the precision of liquid nitrogen generators offers a promising solution to industries in need of high volumes of pure liquid nitrogen. As demands grow and technology advances, this integrated approach is poised to lead the way in the production of this vital resource.