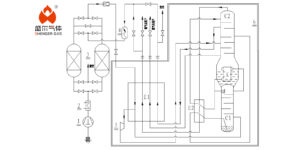
An air separation unit (ASU) is a large-scale set used for nitrogen and oxygen production. Depending on the required gas quantities, the area it occupies can range from several hundred to even thousands of square meters. It involves various chemical and physical principles, and a single unit can have a lifespan of several decades. Therefore, special attention must be paid to its safety and reliability during the design of Air Separation Unit.
Design Principles of Air Separation Units:
- High Safety:
Utilize an internal compression process for liquid oxygen, with the main condenser adopting a bath-type structure and fully immersed operation. This increases the circulation rate of the main cold liquid oxygen, preventing hydrocarbons and other compounds from precipitating on the heat exchange surfaces of the main condenser, which could lead to explosions.
Replace the externally compressed oxygen compressor with an internally compressed liquid oxygen pump, significantly reducing the risk of fire.
- High Reliability:
Our equipment employ efficient booster turbines, effectively recovering the power generated by the turbines. Increasing the unit’s cooling capacity, and significantly reducing system energy consumption.
Our unique dual-layer molecular sieve purification system extends the operational cycle of the unit.
- Adoption of Advanced and Reliable DCS Control System:
Complete air separation units use DCS control systems with redundancy at key control points, ensuring high reliability in the safe operation of the equipment.
Connection Between Air Separation Units and Other Areas
During the initial startup of an ASU, the power plant provides high-pressure steam for driving the turbine and medium-pressure steam for heating. And supplies instrument air for the ASU.
In normal production, the ASU primarily supplies oxygen to downstream gasification units as a feed gas for the reactions. Pressure nitrogen is mainly used in downstream process production as stripping gas, sealing gas, and purge gas.
High-pressure nitrogen is primarily used during the startup and pressurization of downstream purification units.
Characteristics of Modern Air Separation Processes:
- The molecular sieve purification system adopts a dual-layer bed structure. Greatly extending the lifespan of the molecular sieves and reducing bed resistance, making ASU operations safer and more reliable.
- The use of high-efficiency booster turbine technology effectively recovers part of the energy, with turbine cooling efficiency exceeding 85%.
- The adoption of DCS control technology enables integrated control of the central control room, machine room, and local operations. Effectively monitoring the production process of the entire ASU.
These are some design principles and processes of air separation units. Zhejiang Shenger specializes in designing large-scale ASUs. As an EPC contractor for cryogenic air separation, we possess various special equipment installation qualifications. From design, procurement to installation, we handle everything, ensuring our clients can use gas easily and safely!