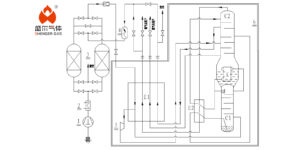
Purifiers play a crucial role in cryogenic air separation units by removing impurities such as water, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons from the air. After the raw air passes through the compressor and precooler, it directly enters the purifier to begin the adsorption of impurities. Subsequently, the air is transferred into low-temperature pipelines. This article provides a detailed introduction to purifiers in cryogenic air separation.
Adsorbents in Purifiers
There are two adsorbers in a purifier, used alternately—one for adsorption, the other for regeneration. The cycle involves single-tower adsorption, equalization, heating for regeneration, cooling, equalization, and adsorption. Therefore, adsorbents are critical for the operation of purifiers, and they must meet the following requirements:
- Porous Material: Adsorbents must be porous substances, with larger surface areas leading to stronger adsorption capabilities.
- High Adsorption Capacity: They must have sufficient adsorption capacity to effectively adsorb the target gases during actual operations.
- High Selectivity: They should efficiently adsorb the target gases while minimizing the adsorption of other impurities to ensure purity.
- Good Stability: Adsorbents must maintain stability despite the significant temperature variations encountered in cryogenic air separation.
- Ease of Regeneration: Reliable regenerability is necessary, as some adsorbents may require periodic regeneration to restore their adsorption performance.
- Good Cyclic Performance and Long-term Stability: They must have good cyclic usage performance, long-term stability, and be cost-effective.
Adsorption and Regeneration Processes in Purifier Operation
Adsorption is a physical phenomenon mainly due to the action of surface forces on the solid surface of the adsorbent. When adsorbed substances approach or collide with the adsorbent surface, they are attracted by the surface forces and adsorbed onto the surface. At the same temperature, the adsorption capacity increases with higher partial pressure.
Regeneration involves using the characteristic that adsorbents have a large adsorption capacity at low temperatures and high pressures, but a small adsorption capacity at high temperatures and low pressures. By applying certain measures, the adsorbed components are driven off the surface of the adsorbent, restoring its adsorption capacity.
The lifespan of an adsorbent can be affected by two main issues. One is breakage, which can result from the inherent strength of the adsorbent, airflow impact, or improper packing. The second is permanent adsorption, where substances such as oil saturate the adsorbent and cannot be desorbed, a condition known as permanent adsorption or “poisoning.”
Operation and Management of Purifiers
Once the air separation unit is operating normally, the purifier enters a normal automatic switching process. Operators need to closely monitor the following aspects:
- During purifier operation, regularly check the temperature curves at the outlet of the electric heater and the purifier outlet to ensure the purifier completes heating and regeneration within the specified time. Also, monitor the CO2 content at the outlet of the adsorption column to determine if the purifier is operating normally.
- Closely monitor whether the purifier’s operating procedure is normal and if the valves are operating responsively.
- Pay close attention to the inlet air temperature of the adsorption column to ensure it is within the normal range.
- After two years of operation, inspect the breakage condition of 13X molecular sieve and activated alumina, and replace them entirely if necessary.
- Monitor the pressure difference in the purifier closely. If the pressure difference is too large, promptly clean or replace the filters.
There have been numerous incidents both domestically and internationally where poor purifier performance led to production stoppages or even explosions in the main condenser, underscoring the importance of attention to these details. Key focus areas include the inlet temperature of the purifier, the outlet dew point, and the CO2 content.